A localized dust storm on Mars may have played a key role in driving water into the planet’s upper atmosphere, offering fresh clues to how the Red Planet lost much of its water over billions…
From fungi to humans, ‘smart valves’ assist communication…
[caption id="attachment_14298" align="alignnone" width="620"] The new research relied on an apparatus devised by Edwin Chapman and his colleagues that can, for the first time, record exactly when the fusion pore opens and closes. PHOTO: DAVID…
HKBU study reveals human skin flakes lead to…
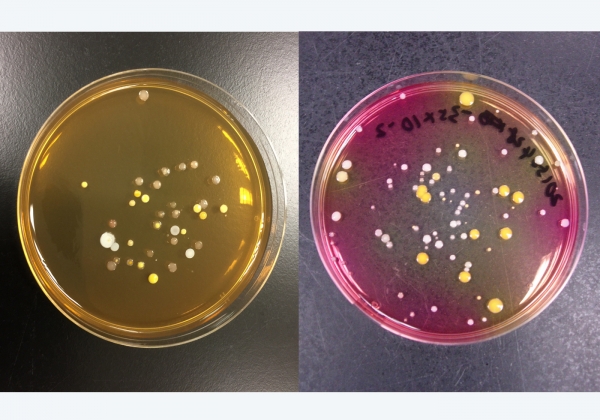
Skin squames are a source of food for the bacteria found in air-cooling units, which produce odours even in a dust-free air-conditioning system, a research by Hong Kong Baptist University scholars revealed. [caption id="attachment_14290" align="alignnone"…
Two-stage gas sensor reports on soil dynamics
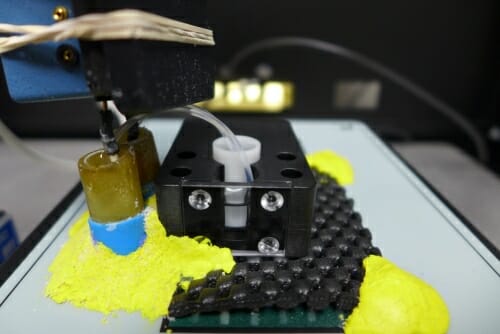
Rice University's next-level, nondisruptive biosensor delivers robust report on microbes' health, activity [caption id="attachment_14286" align="alignnone" width="947"] Rice University graduate student Hsiao-Ying (Shelly) Cheng led a project to develop two-stage microbial sensors that can observe and…
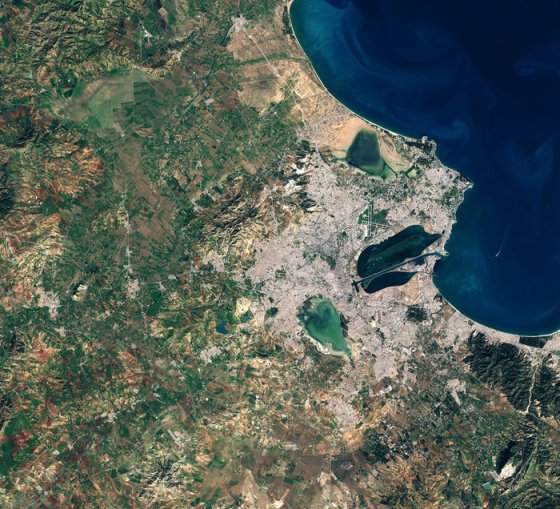
Tunis wetlands
[caption id="attachment_14283" align="alignnone" width="657"] Credit: contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2017), processed by ESA[/caption] This Copernicus Sentinel-2 image features Tunisia’s capital Tunis, in North Africa, and highlights some of the country’s important wetlands. Captured on…