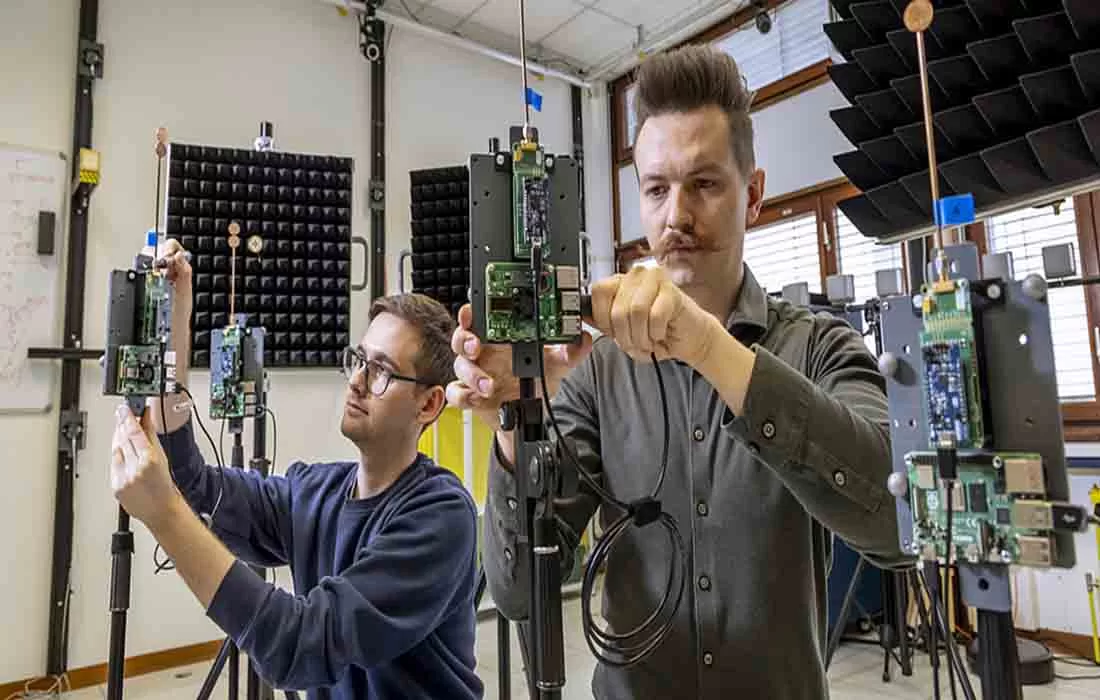
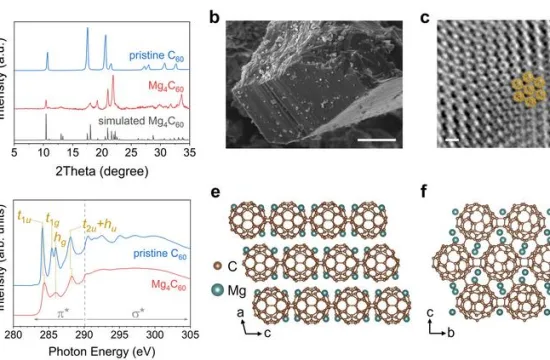
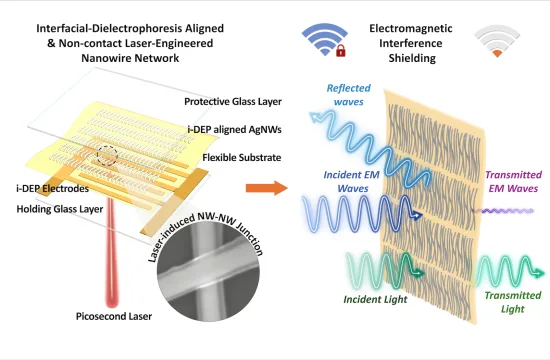
Brussels, August 28 — A European research initiative is exploring how to eliminate the need for batteries in Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
The Ambient-6G project, backed by €8.4 million in funding from the European Union, brings together leading universities and industry partners to develop sustainable, self-powered IoT technologies.
Led by a consortium including Graz University of Technology, Aalto University, KU Leuven, and the University of Oulu, the project seeks to harness environmental energy sources—such as heat, vibrations, and radio waves—to power IoT devices wirelessly.
With an estimated 20 billion IoT devices currently in use and projections suggesting that number will double by 2033, the environmental burden of battery waste is a growing concern.
The Ambient-6G team is pioneering a new communication method known as energy-neutral backscatter communication. Unlike traditional IoT devices that actively transmit data via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks, backscatter devices reflect signals from central antennas, subtly modifying them to encode information.
“This passive approach eliminates the need for an active transmitter,” said Klaus Witrisal, head of the Institute of Communication Networks and Satellite Communications at Graz University of Technology. “The energy harvested from radio waves is enough to operate the device.”
To support this technology, researchers are developing distributed antenna systems that minimize transmission power and reduce environmental radiation exposure. These antenna arrays enable efficient communication with self-powered devices across large areas.
Real-World Applications and Challenges
Potential applications for battery-free IoT devices are vast. In retail, electronic price tags could operate without batteries, reducing waste and maintenance. In logistics, goods could be tracked with high precision—even in expansive warehouses.
However, challenges remain. “Backscatter communication involves extremely weak signals, especially over long distances,” Witrisal explained. “We’re working on advanced algorithms to extract meaningful data from noisy environments.”
The Ambient-6G project represents a major step toward a more sustainable IoT ecosystem, with implications for energy efficiency, environmental impact, and technological innovation. If successful, it could redefine how billions of devices are powered and connected in the future.