A rural art fair’s grassroots-led, mindful, and immersive travel experience embodies a revitalizing tourism approach that a study found has built community resilience, strengthened local identity, and re-energized daily life in a Japanese island village grappling with decline.
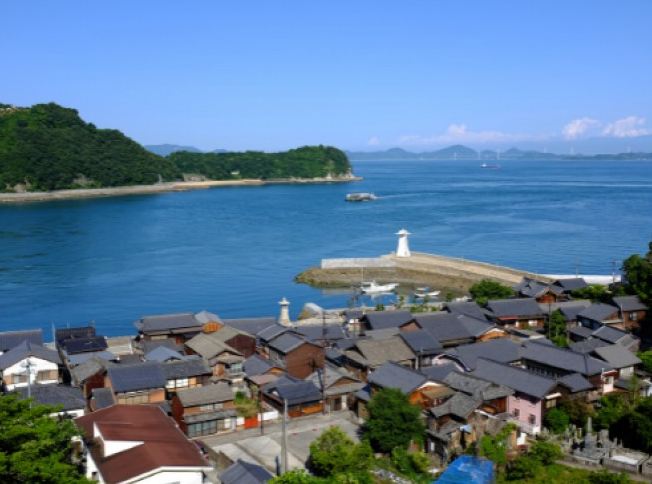
Mitarai, on the east coast of Osakishimojima Island in the Seto Inland Sea, is a sample of a peripheral community in Japan facing depopulation, aging, and socioeconomic decline, a phenomenon that the study said is symptomatic of late capitalism in many developed nations where the decline of outlying areas is predominant.
Wedged between Honshu, Kyushu, and Shikoku, three of Japan’s four main islands, the Seto Inland Sea is home to around 3,000 smaller isles, a dozen of which serve as festival venues of one of the country’s biggest art fetes, the Setouchi Triennale.

“My early seven published peer-review research in English already highlighted the role of how big-scale art festivals like Setouchi Triennale can help to facilitate regional revitalization through art tourism and in-migrant micro-entrepreneurship,” said the study’s lead author Hiroshima University Assistant Professor Meng Qu from the Graduate School of Humanities and Social Sciences’ Department of Integrated Global Studies.
“Nowadays, Setouchi Triennale has already become a successful model of art tourism revitalization for the Japanese government. There are more than 100 rural art festivals established in Japan influenced by this art rural placemaking trend.”
However, under this type of optimistic background, Qu said that his research on big-scale art fairs showed that community-level outcomes are highly divergent between villages and islands.
“Some islands are revitalized by newcomers and art businesses. But on some islands, nothing has happened. This brought me another thought — large-scale art festivals revitalization is not the only option or panacea for diversified rural communities,” he said.
Together with Wakayama University Professor Joseph Cheer, Qu researched small-scale community-engaged bottom-up type of art fairs exemplified by Mitarai’s Shiosai art fest. This week-long community art fete has been held since 2017 to rejuvenate the village.
The researchers explored the extent to which bottom-up art events in small rural communities can serve as a vehicle for sustainable development. And examined the specific challenges of employing bottom-up art events in small, rural community contexts.
“The links between art events and sustainable development in rural contexts where revitalization is pressing is becoming increasingly obvious,” the researchers said in their paper.
“Findings suggest that the Shiosai drives visitation to the area and has reinvigorated latent cultural heritage. The festival stimulates inward migration and enhances community resilience and vital social capital.”
The researchers found that the festival puts a premium on upholding and considering local opinions as well as valuing the area’s history, culture, and architecture. Activities are not limited to art but also in pursuits that help safeguard local collective memory through co-learning, reinvigorate dwindling agriculture through “half-agriculture and half-art crafts” experiences, and enliven the atmosphere by revitalizing and re-using abandoned old buildings.
The festival also attracted creative in-migrants and succeeded in nurturing social connections with artists from neighboring regions and partnerships with both local businesses and nearby universities.
“In Mitarai, the focus is on the local community playing a central role, emphasizing meaningful social engagement, co-creation, and co-development,” they said.
“The nuanced focus on art festivals in declining rural areas helps advance festival studies where for the most part, focus has tended to be on urban and large-scale festival tourism developments or elite art placemaking in rural contexts towards community-engaged events.”
But as the festival is driven from the bottom-up without external support, the researchers noted that the extent of future local-level involvement remains a critical success factor.
“The implications suggest that community engagement is a vital ingredient in the mobilization of festivals in rural contexts, as well as in ensuring that sustainable development outcomes can be optimized.”
Their study is selected in the December 2021 special issue of the Journal of Sustainable Tourism. Their findings were first published online by the same journal in December 2020.