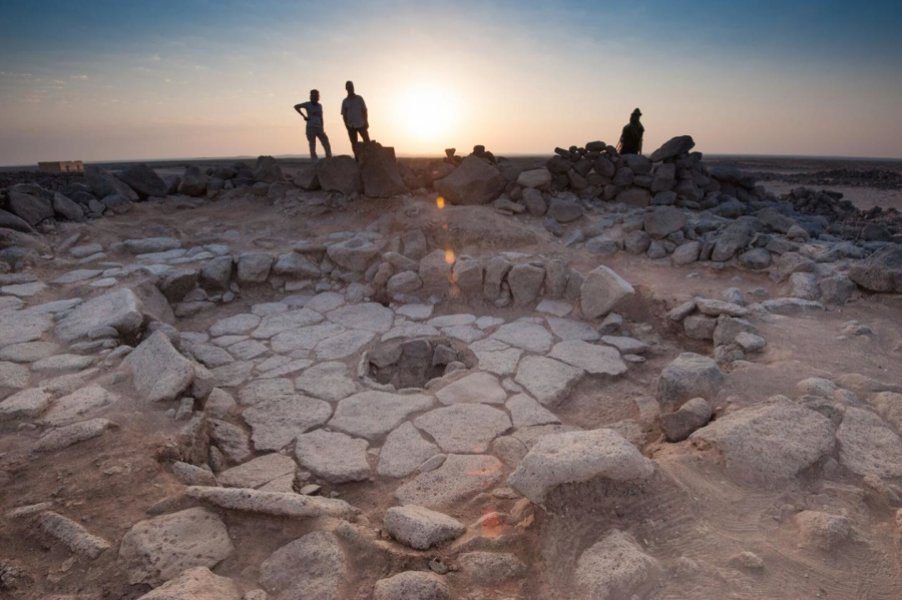
A team of researchers from the University of Copenhagen, University College London and University of Cambridge have analysed charred food remains from a 14,400-year-old Natufian hunter-gatherer site—a site known as Shubayqa 1 located in the Black Desert in northeastern Jordan.
A team of researchers from the University of Copenhagen, University College London and University of Cambridge have analysed charred food remains from a 14,400-year-old Natufian hunter-gatherer site—a site known as Shubayqa 1 located in the Black Desert in northeastern Jordan.
The results, which are published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, provide the earliest empirical evidence for the production of bread:
“The presence of hundreds of charred food remains in the fireplaces from Shubayqa 1 is an exceptional find, and it has given us the chance to characterize 14,000-year-old food practices. The 24 remains analysed in this study show that wild ancestors of domesticated cereals such as barley, einkorn, and oat had been ground, sieved and kneaded prior to cooking.
The remains are very similar to unleavened flatbreads identified at several Neolithic and Roman sites in Europe and Turkey. So we now know that bread-like products were produced long before the development of farming. The next step is to evaluate if the production and consumption of bread influenced the emergence of plant cultivation and domestication at all,” said University of Copenhagen archaeobotanist Amaia Arranz Otaegui, who is the first author of the study.
University of Copenhagen archaeologist Tobias Richter, who led the excavations at Shubayqa 1 in Jordan, explained:
“Natufian hunter-gatherers are of particular interest to us because they lived through a transitional period when people became more sedentary and their diet began to change. Flint sickle blades as well as ground stone tools found at Natufian sites in the Levant have long led archaeologists to suspect that people had begun to exploit plants in a different and perhaps more effective way.
But the flat bread found at Shubayqa 1 is the earliest evidence of bread making recovered so far, and it shows that baking was invented before we had plant cultivation. So this evidence confirms some of our ideas. Indeed, it may be that the early and extremely time-consuming production of bread based on wild cereals may have been one of the key driving forces behind the later agricultural revolution where wild cereals were cultivated to provide more convenient sources of food.”
Charred remains under the microscope
The charred food remains were analysed with electronic microscopy at a University College London lab by Ph.D. candidate Lara Gonzalez Carratero (UCL Institute of Archaeology), who is an expert on prehistoric bread:
“The identification of ‘bread’ or other cereal-based products in archaeology is not straightforward. There has been a tendency to simplify classification without really testing it against an identification criteria. We have established a new set of criteria to identify flat bread, dough and porridge like products in the archaeological record. Using Scanning Electron Microscopy we identified the microstructures and particles of each charred food remain,” said Gonzalez Carratero.
“Bread involves labour intensive processing which includes dehusking, grinding of cereals and kneading and baking. That it was produced before farming methods suggests it was seen as special, and the desire to make more of this special food probably contributed to the decision to begin to cultivate cereals. All of this relies on new methodological developments that allow us to identify the remains of bread from very small charred fragments using high magnification,” said Professor Dorian Fuller (UCL Institute of Archaeology).